Nutrition
How Important Are Omega-3s?
It’s difficult to escape the diet community talking about the absolute necessity of getting omega-3s on your plate. They’ve been linked to reducing cardiovascular diseases, cancer, depression and a host of other diseases time after time. Many of this evidence has been found to be inconclusive and people are wondering what all the fuss is about. Is there any truth to it? Does eating omega-3s really make a dramatic difference to your health and if so has anyone actually tested this theory?
The answer is yes. Paul Greenberg, author of American Catch and Four Fish, spent a year documenting whether eating fish every day had any real impact on his health. In the Frontline documentary, The Fish on My Plate, Greenberg met a doctor before and after his experiment in order to track the results.
Before the experiment, Greenberg suffered with elevated blood pressure, cholesterol, depression and sleep issues. “I started to listen to the soft purr of the omega-3 industry: This is everything they’re supposed to fix” he says in the documentary.
After a year of this daily fish diet, it was revealed that Greenberg’s cholesterol ratio and his triglyceride level was the same. In fact, his blood pressure increased and he had higher mercury levels which a biologist told Greenburg was “slowing your thinking and hurting your memory”.
– RELATED: 3 Foods That Will Reduce Inflammation –
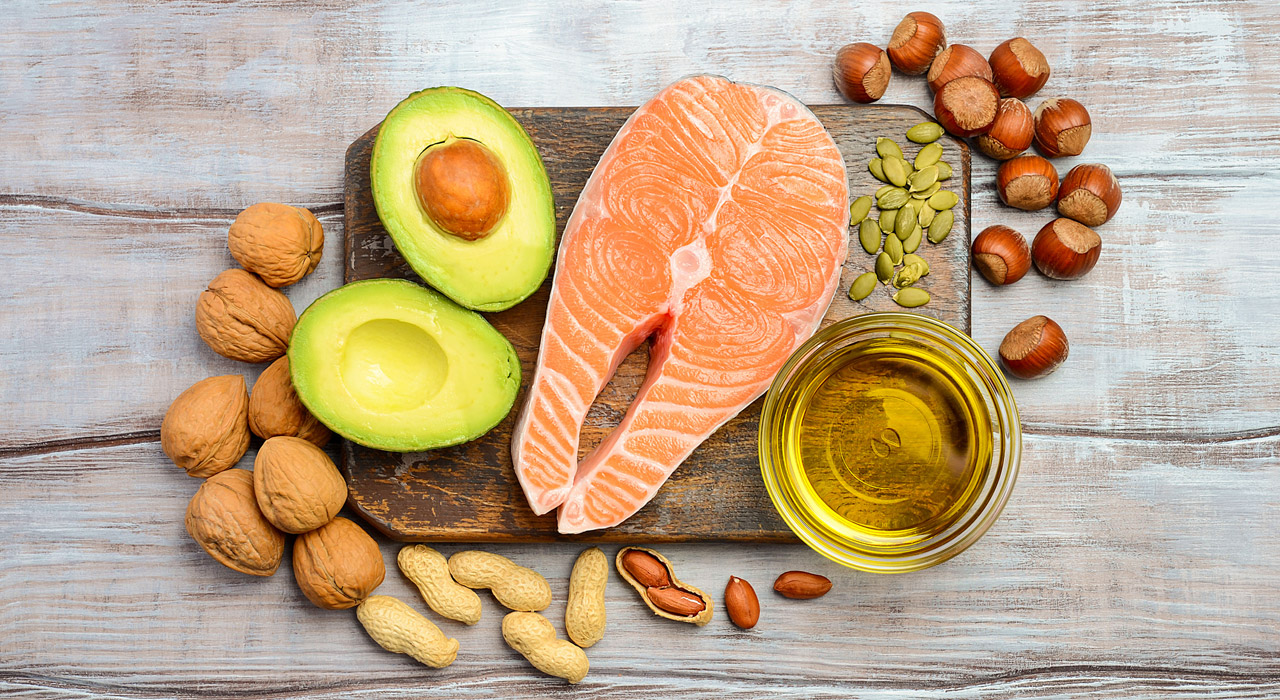
What are omega-3s?
Just in case you’ve got this far down and are wondering what omega-3 even is, let us remind you. Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats. The two main are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are primarily found in fish. The other type is alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) which can be found in nuts, flax seeds, vegetable oil and hemp.
There isn’t any standard recommended dose, however some recommend a daily dose of 250 to 500 milligrams(mg) of EPA and DHA for healthy adults.
What can we believe?
This study might leave you thinking that it’s all ‘fake news’ and you’ll never listen to the diet community again. The FDA, however, only recommend you eat fish 2-3 times a week as all fish contain a trace of mercury which can put your health at risk. Also, this study may have concluded that Greenberg did not benefit from any of the health benefits that omega-3s promise, but that does’nt mean someone else won’t.
Furthermore, many of the claimed health benefits, including a reduction in depression are, in general, small and inconclusive. What we do know, however, is that there is strong evidence that omega-3s ‘may improve cardiac function by their anti-triglyceridemic, antihypertensive, hemostatic, antiarrhythmicanti-atherogenic effects.’ Simply put, omega-3s, when incorporated into a healthy lifestyle, can play a prominent part in good cardiovascular health.
Just like salt, sugar, protein and fats, omega-3s are an important part of a balanced diet. Incorporating fish in your diet is one way to ensure this, however it isn’t the only way. Get your omega-3 fix elsewhere. Foods such as wild rice, eggs, walnuts are full of them. Be wary of sourcing this ‘superfood’ through supplementation such as fish oils capsules, however. There is a strong lack of evidence that fish oils supplements help to prevent cardiovascular diseases. The best way to source any nutrient is through good old fashion food.
For nutritional advice and more sign up to the TRAIN for HER newsletter.